Table of Contents
Definition
Checksheet is a data collection tool. It is an analytical tool used to collect, record, and present data for the objective of conducting analysis.
Checksheet is used to collect both quantitative and qualitative data. When Check-sheet is used for collecting Quantitative data it is generally called a Tally Sheet.
Data Collection is the primary step for any improvement identification or problem analysis. It is one of the 7 QC tools. Following are the other 7 QC Tools
- Histogram
- Pareto Chart
- Stratification
- Fishbone Diagram
- Control Chart
- Scatter Diagram
Generally speaking, Check-sheet acts as an input for other QC tools. The first step of any problem solving is to do Gemba(i.e. To go on the shop floor and see the problem at the site.) and collect data using a check-sheet.
What are the types of Checksheet?
Types of the checksheets are majorly based on the type and purpose of data collected. Following are the types of checksheets:
Classification Checksheet
A classification checksheet is used to collect data in a categorized form. Categorizing collecting data makes it very useful.
Suppose our health department wants to see if different types of viral fevers have some relation with the month of the year, they would use a classification checksheet for collecting that data.
To understand the usefulness of this type of check-sheet, imagine if only data for the number of cases for viral fever are collected and not the month of the occurrence. Will the data be useful? I guess no.

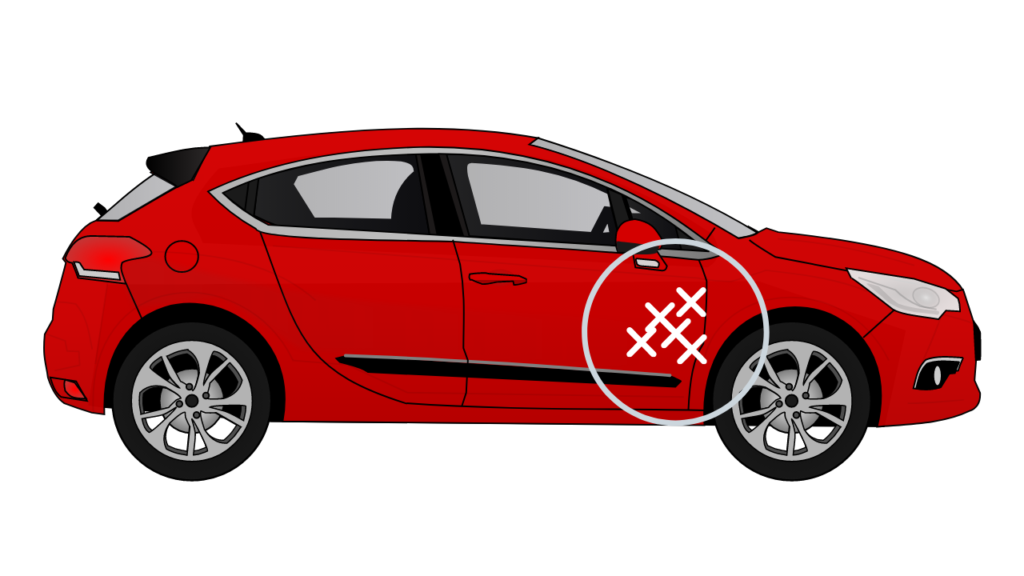
Defect Location CheckSheet
A defect location checksheet helps identify the problematic areas precisely. This type of checksheet uses product illustration or image for data collection.
The defect location check-sheet not only counts the number of defects but also reveals areas where most of the defects occur.
This type of checksheet usually helps identify visual defects. For example, if we are checking our car painting(Red paint) process using this type of check-sheet and we find White spots on a particular area in most of the defective parts, we would directly look into the system or machinery responsible for painting that area of the car rather than analyzing the complete painting process.
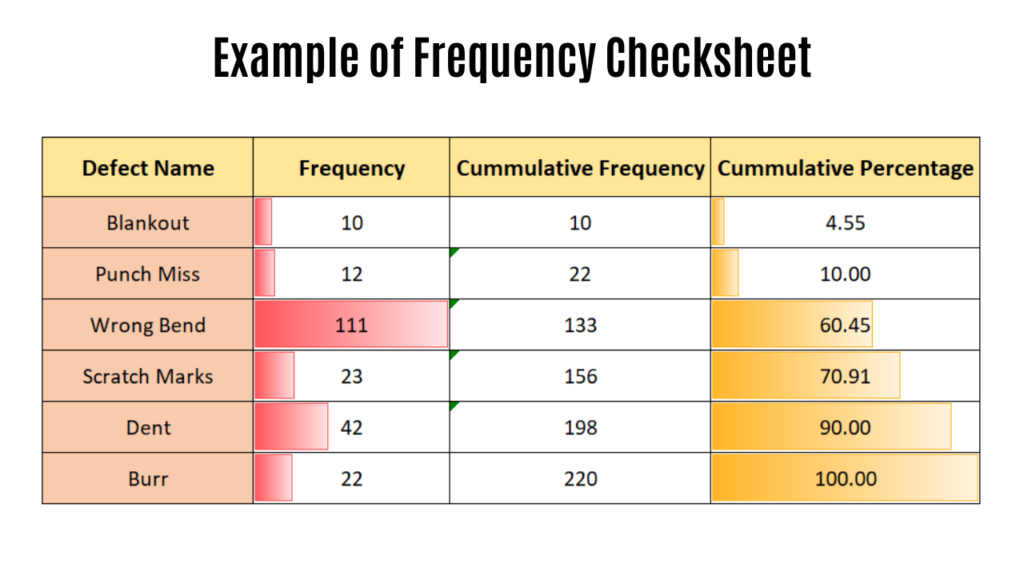
Frequency Checksheet
The ultimate goal of any improvement activity is to get maximum improvement with the least amount of effort. That could be done when we are focusing on the highest frequency problem i.e. problem or defect occurring the maximum number of times. Pareto distribution is a beautiful example of this kind of prioritization.
Frequency checksheet Comes in handy in such a situation for collecting the frequency of occurrence.
This check sheet is useful in getting defect frequency distribution for the process being monitored.
For example, if we are monitoring a Sheet metal process we might be interested in finding out which type of defect is occurring the most frequently. So that action can be initiated to improve upon that particular problem.
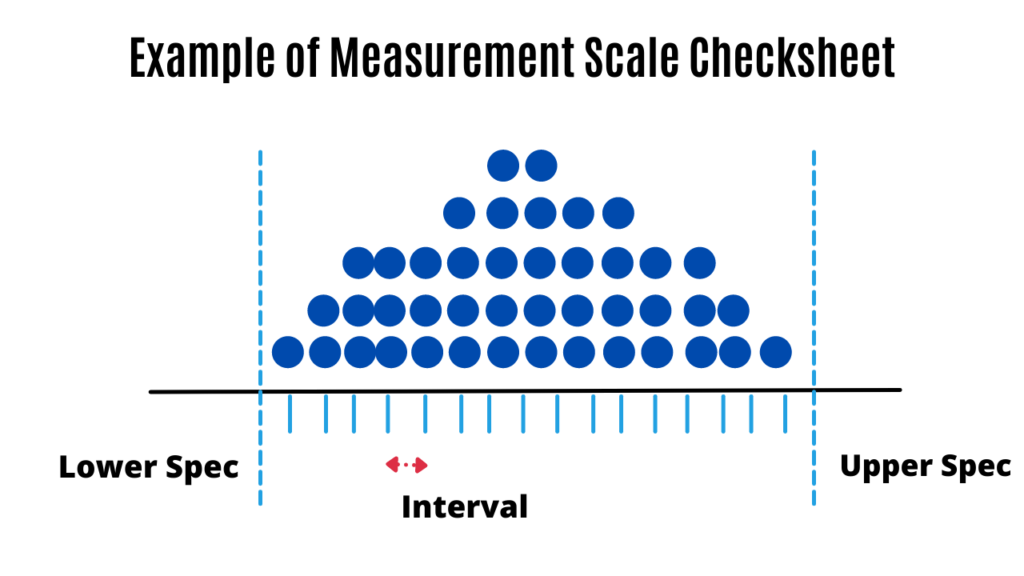
Measurement Scale Checksheet
A measurement scale is divided into intervals and measurements are indicated by checking an appropriate interval.
This type of check sheet provides a visual description of the probability distribution, which helps get a better idea of Process capability and performance.
Read more about Process Capability Analysis here.
Looking at the probabilistic distribution helps immediately identify outliers in the data and figure out if a specific area needs extra adjustment.
What are the benefits of a Checksheet?
We make multiple decisions on a daily basis and those decisions impact the output product, in terms of quantity and quality. Data collected from our processes is the input for taking all these decisions. Checksheet is a very useful tool for collecting this data in an effective way. Following are some of the benefits check sheets provide
- Checksheets facilitate and document the Data Collection process.
- Facilitates data collection in a systematic and organized manner.
- Helps collect data in a processable form by processable I mean data from which one or multiple inferences could be drawn.
- Checksheet is a simple and effective way to display data.
- Acts as input for multiple 7 QC tools such as pareto,histogram,etc.
- It helps identify frequency of defect occurrence.
- Quantify defects by type location And cause.
What is the Difference between Checklist and Checksheet?
Check-sheet and CheckList look and sound similar, hence people confuse them for each other, but they are completely different.
Checksheet is a data collection tool whereas a Checklist is a tool to make sure all steps of a particular process are completed and not missed.
The purpose of a checksheet is to collect data in a systematic and organized manner but a Checklist is used for a totally different purpose. It is used as a kind of Poka-Yoke or mistake-proofing tool to avoid missing an important step in any of the processes.
We use checklists all the time. When we plan a trip and the list we make of all the things we need to carry during our trip is an example of a Checklist.
Procedure for Making Checksheet
- Step 1## Decide what event or problem will be observed.Develop Operational definitions.
- Step 2## Decide when data is to be collected and for how long.
- Step 3## Design the form.Design it in such a way that data need not to be Re-copied for the analysis purpose.
- Step 4## Test the check sheet.Take a short trial to ensure that appropriate data is being collected and the check sheet is simple to use and maintain.
Where do we use Checksheets?
As I described earlier, checksheets are classified based on the type of data being collected and the purpose for which it is being collected.
So Checksheets can be used in multiple ways but the most popular uses of Checksheet are as follows
- For Making Pareto distribution of defects.
- Used for process performance monitoring.
- For regular Production Recording.
- Input for various other QC tools.
Above stated applications are not exhaustive but only indicative of the fields of application for Checksheets.
Is Checksheet one of the 7 QC tools?
Yes, the checksheet is one of the 7 QC tools. It facilitates and documents the data collection process.
The data collected using the checksheet acts as the input for various other 7 QC tools such as Histogram, Pareto, Scatter Diagram, etc.




