Table of Contents
What is a Process Control Plan?
Customer is the core focus of any business, hence keeping customers happy shall be your first priority if you want your business to sustain and to grow. There is only one way to keep customers happy that is to provide them good quality products. A control plan helps you achieve it.
Producing good quality products need a robust and Controlled process. The control plan provides an overview of all the controls in place along with the process steps.
A control plan is a document that layout various methods that are taken for quality control of each manufacturing process involved in part Production. To be precise, it is a document that outlines all quality controls placed on each process input to obtain the desired output. In more simple terms, a Control plan provides the operator, foreman, or inspector detailed information required to control the process and to produce desired quality products.
Control Plans are currently being utilized to ensure product quality in multiple industries, such as Automotive, Electronics, Aerospace, Heavy Equipment, and many other industries throughout the world.
In my experience, most of the manufacturing companies are using control plans but very few of their employees completely understand the what, why, how aspects of control plans. In this article, I have covered all these questions and much more.
Why do we need a Control Plan?
The implementation of control plans has several benefits. If you are a manufacturing unit you should implement control plans for all your products and processes to reap these benefits.
Waste reduction and increased consistency
Implementation of a Control plan helps reduce waste. The control plan outlines critical areas of focus in the manufacturing process that need to be controlled to maintain product quality.
Control Plan helps reduce waste by identifying sources of variation and establishing controls to monitor them. Control Plan highlights or focuses critical to quality parameters, which indeed help reduce rejection, scrap, and other types of waste.
Example: Let us take an example of the M6 Bolt. Pitch diameter is one of the most critical parameters in bolts, for it to function properly. Hence control plan for Bolt production would incorporate checking of pitch diameter in setup approval of the rolling process.
Let us assume the Rolling die/Tool has worn out and would produce parts with pitch diameter out of specification. If there is no control plan or control on the setup process, we would come to know about defects only after the customer reports it. All the material produced would be rejected and would cost the company a huge sum. On the other hand, if the Process control plan was prepared and controls were established it would have been caught at the setup process itself.
Guide for Operators
A control plan acts as a roadmap or guide for operators at various production processes. It covers all critical parameters, various controls, the frequency at which an operator has to check, etc.
Control Plan contains answers to most of the questions that might arise in the operator mind during processing production parts. It’s like the frequently asked question section of the college website.
Focus on Customer Requirements
The control plan highlights customer requirements in the form of critical parameters and outline methods to control them. Moreover, Assure reaction plans are in place in case of out-of-control conditions.
What are the three types of controls of a control plan?
Control plans can be divided into three types based on the stage of development.
- Prototype Control Plan – This type of Control plan is prepared at an early stage of development. Prototype Control Plan includes descriptions of the characteristics to be measured and the material and performance tests to be completed during the prototype build.
- Pre-Launch Control Plan – Pre-Launch Control Plan should contain descriptions of the characteristics to be measured and the material and performance tests to be completed after prototype but prior to final product launch and regular production
- Production Control Plan – Production Control Plan should contain a comprehensive listing of the product and process special characteristics, the process controls, measurement methods, and tests that will be performed during regular production
What are the inputs required for preparing a control plan?
Control plans can’t be made in isolation. Control plan preparation needs multiple inputs. To make an effective control plan, we need to collect all relevant process information and need to absorb all that information to make a solid control plan.
First of all, to make a control plan, CFT has to be constituted. Inputs of each section of the part production process are equally important. Making a cross-functional team is the best way available to take those inputs from multiple departments/Sections.
The information contained in the control plan originates from multiple sources. I have listed down a few of these sources. This list is exhaustive but not complete. There can be additional sources but the list mentioned below covers all major ones.
•FMEA(Failure mode and effect analysis)
•Flow Chart (process sequence)
•Lay-out Plan production line
•Sequence Of Events
•Part Number/ Tooling / Tool List
•Assembly Drawing
•Specifications/ Dimensions/ Tolerances
•CTQ List
•Process Map
Inputs from all of the above mentioned sources are important.
For Example, FMEA encapsulates all past failures, hence we can avoid repetition of any of those problems by establishing proper control for causes of those problems, in the control plan.
What are the steps in setting up a Process Control Plan?
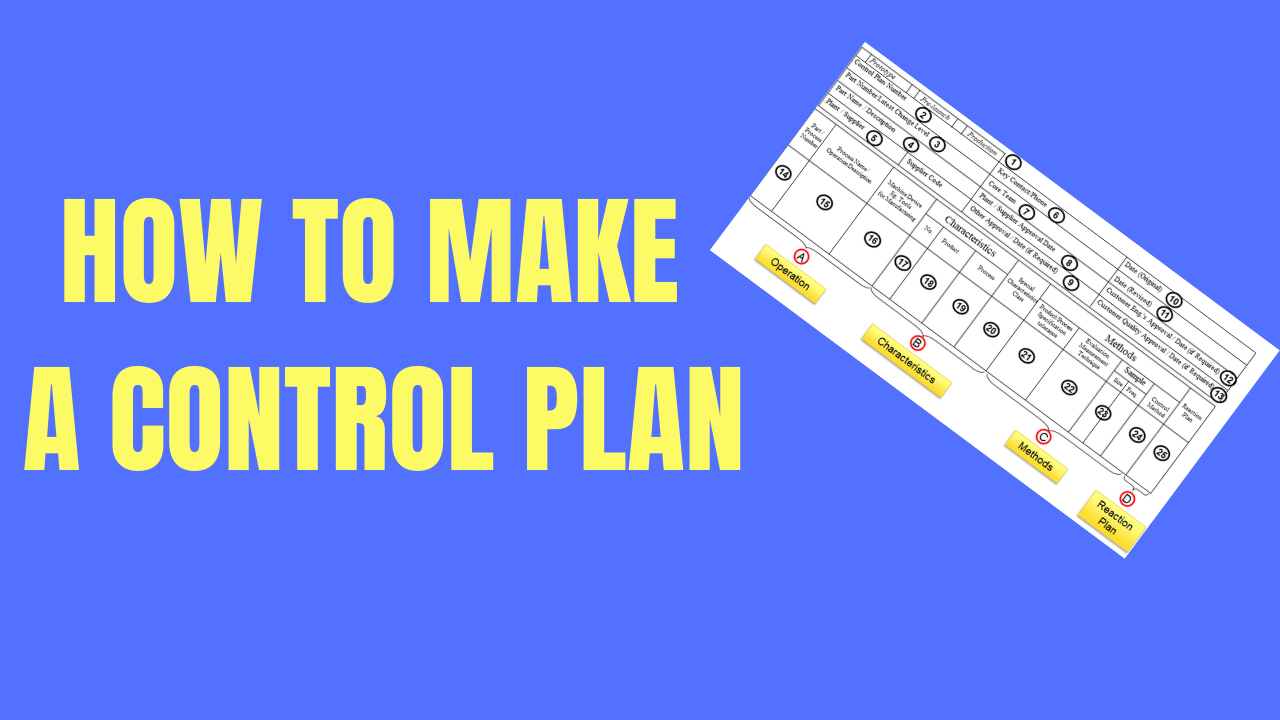
On the macro-level structure of control plan can be divided in two sections. General information and main content. The main content can be further divided into four parts operation, characteristics, Methods, and Reaction plan.

Now i will explain each section briefly
Basic or General Information
At the header of a Control Plan is general information. I could vary from organization to organization.
- Type of Control Plan
Whether control plan is proto type,Pre-Launch or Production.
- Control Plan Number
A document number or unique number designated to control plan based on the procedure of Control of records.
- Latest change level/Part Number
Identification number of the output product of the process.
- Part Name/Description
Identification name of the output product of the process.
- Plant/Supplier
It describes the plant of production or Supplier name in case of the outsourced part.
- Key Contact Person
It describes the name of the contact person.
- Core Team
In this section the name of all the CFT members is covered.
- Plant/Supplier Approval Date
In this field date of approval document approval is mentioned.
- Other Approval date(if required)
It describes any other approval date if any.
- Date(original)
Data of original release
- Date(Revised)
The number used to control revision of the document
- Customer Eng.’s Approval / Date (if Required)
Sign of Customer engineering representative. Write NA in case not applicable.
- Customer Quality Approval / Date (if Required)
Sign of Customer quality representative.Write NA incase not applicable.
Content Section
Operation
14. Part/Process Number
Usually referenced from the process flow chart, PFMEA, or Tool sheets. It is the operation number or process number.
15. Process Name/Operation Description
Identify the process/operation that best describes the activity being addressed (e.g. work elements) in the respective processes.
16. Machine, Device, Jig, Tools for Manufacturing
Identify the processing equipment required. (e.g.If Sheet metal process is there machine would include power press, device, jig power tools, assist arms, conveyors, etc.)
Characteristics
17. Number
Depicts sequence number for product and process characteristics.
18. Product Characteristic
Distinguishing features and/or attributes of products as per customer specification.For example,Outer Diameter,Total Length,etc.
19. Process Characteristic
Characteristics of the process used to control the process, so that variation in product parameters can be minimal. For example, Hydraulic Pressure, Mould Temperature, etc.
20. Special Characteristic:
key parameters, which are critical to quality, and any deviation in these parameters could have serious repercussions. Generally, the customer defines critical parameters in part drawing itself but based on your past experience additional special characteristics can be defined.
Methods
21. Product/Process Specification:
Specifications/tolerance for a part or process. Generally, Product specifications are customer-defined. (Except for proprietary parts),Process specifications are based on past experience or process validation trials.
22. Evaluation/Measurement Technique:
Identifies the measurement system being used to measure product/process characteristics. (eg. gages, fixtures, test equipment, blocks, go/no go, etc)
23. Sample Size/Frequency:
Describes the sample size(i.e. How many parts have to be checked?) and Frequency(i.e. At what interval that characteristic has to be checked.) (eg. size: 5 pieces/frequency: at every 2 Hours)
24. Control Method:
Brief description of how the operation will be controlled.For example, Daily preventive maintenance checksheet, Setup checksheet, etc.
Control could be a process or product control. It can be further divided into prevention control or detection control.
As a thumb rule,focus on following points,while deciding control type.
process control rather than product control
prevention rather than detection
targeting nominal rather than specification limits
Reaction Plan
25. Reaction Plan:
As the name suggests it describes the action, that needs to be taken in case characteristic goes out of control. It is a kind of instruction for first aid.
Examples
-Call supervisor
-100% Inspection until the process is back in control
-Calibrate equipment
-Replace Drill




Aw, this was an extremely good post. Spending some time and actual effort to make a superb article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and never manage to get nearly anything done.
Pingback: What is the Production Part Approval Process(PPAP)? | Free Templates - Quality Blog