Table of Contents
Definition
APQP stands for “Advanced Product Quality Planning”.APQP is a structured and documented method of defining and establishing the steps necessary to assure that the product satisfies customer requirements.
APQP is one of the 5 Core Tools. The other four are PPAP, FMEA, SPC, and MSA.
Product Quality Planning involves logical sequencing of development events which ensures on-time development, with the least amount of waste and increased customer satisfaction.
The goal of Product quality planning is to facilitate communication with everyone involved(supplier as well as Customer) to assure that all required steps are completed on time.
Also, APQP provides a standardized set of requirements, which customers can communicate to the suppliers. It helps instill confidence in customers that suppliers are following standardized practices and hence ensures uniform production quality trends.
Key Takeaways
- APQP stands for Advanced Product Quality Planning.
- APQP is one of 5 core tools recommended by IATF 16949:2016.
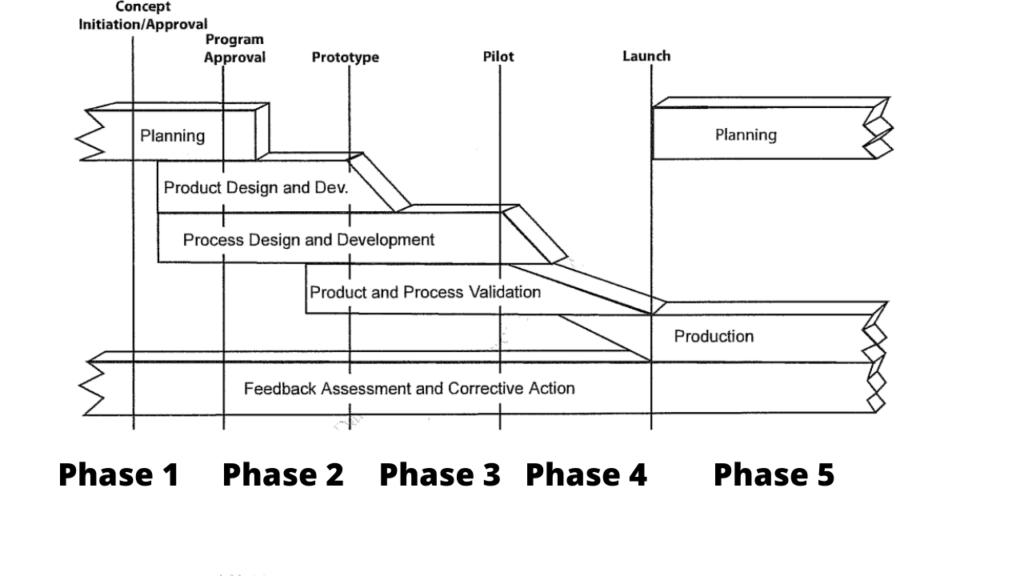
- APQP has five phases.
- Objective of Phase 1 of APQP is to determine customer needs and define Quality Program.
- Objective of Phase 2 is to convert design features and characteristics into a near-final form.
- Objective of Phase 3 is to ensure the comprehensive development of an effective manufacturing system.
- Objective of Phase 4 is to validate the manufacturing process through a detailed evaluation of significant production run.
- Objective of Phase 5 is to take feedback from the manufacturing stage and improve the current process.
Five Phases of APQP
Phase 1 : Plan and define
The Goal of any product development program is to meet customer needs while providing competitive value. In this phase customer Expectations and needs are taken into consideration for Planning Product Quality, so that all customer-specific requirements are met.
Although plan and define phase activities vary based on customer needs and expectations, product type, etc. But general recommendations provided by AIAG are as follows.
In short Phase 1 of APQP has two objectives
- Determine Customer Needs
- Define and Plan a Quality Program
Inputs for the Phase 1
1.1 Voice of Customer
The “Voice of Customer” encompasses inputs from internal or external customers in the form of complaints, recommendations, or information. There are multiple ways of collecting Voice of Customer following are few amongst them
#1 Market Research
The customer is the center point of any business intent. So it becomes all more important to understand the voice of the customer. Multiple tools can be used to understand the Voice of the Customer.A few of them are as follows
- Market Surveys
- Customer Interviews
- New Product quality and reliability studies
- Benchmarking
#2 Historical Defect,Warranty and other Quality information
One should not make the same mistake twice, since repeating the same mistake is foolishness. If we are aware of our previous mistakes or issues it is more likely not to be repeated.
These mistakes shall be considered as an extension of design requirements and included in the analysis of the customer needs.
Past defect history shall include but not be restricted to the following options
- Warranty reports
- Inhouse Complaints
- Development time issues
- Expected defects considering Product category
- Supplier Plant internal quality reports
- Process capability studies data
- Quality Function Deployment(QFD) Projects
#3 Customer Observations
Customer-reported issues shall be on the top of our focus list. Repetition of the same issue at the customer end could have serious implications on your current as well as future business.
In fact, customer-reported defects are the most direct form of Voice of Customer.
#4 Audit Observations
Audits act as lubricating oil in an organization’s machinery, necessary for its smooth running.
Audits could be internal such as QMS Audit, Product and Process Audit, or External such as Customer audit, International certification Body audits. Observations from all these audits shall be incorporated in the Product Quality Planning to avoid the repetition of similar problems.
1.2 Business Plan and Marketing Strategy
Understanding business plan and marketing strategy are important to understand various constraints for drafting a Product Quality Plan.Constraints such as cost,time,investment,etc.
1.3 Product/Process Benchmark Data
Benchmarking is the process of comparing the current state of the product, process, or service with other outstanding and best in industry products, processes, and services. In some cases, the comparison will be with other divisions within the same company and in other cases, external comparisons such as Industry peers, a competitor, or similar industry players are more appropriate.
Benchmarking acts as an extremely helpful input for Product Quality Planning..
To read about Benchmarking in detail: Click Here
1.4 Product/Process Assumptions
There will ve assumptions that the product has certain features, design, or process concepts. These include technical innovations, advanced materials, reliability assessment, and new technology. All should be utilized as inputs.
1.5 Product Reliabilities Studies
This type of data considers the frequency of repair or replacement of components within a designated period of time and results from long-term durability and reliability tests.
1.6 Customer inputs
Customers can have additional requirements not covered in any of the APQP steps. Such requirements shall be captured in the form of the Customer Specific Requirement Matrix and shall be taken as input while drafting the Product Quality Plan.
Outputs from the Phase 1
1.7 Design Goals
Design Output is an output of the first phase of APQP. Design goals are the conversion of the voice of the customer into measurable design objectives. It includes things such as the material composition of the product.
1.8 Reliability and Quality Goals
Reliability goals are established based on customer wants and expectations, program objectives, and reliability Benchmarks. An example of a reliability goal would be no crack in Engine valve springs over 10 million cycles.
1.9 Preliminary Bill of Materials
A preliminary bill of material based on product and process assumptions shall be drafted and shall include a potential list of suppliers.
1.10 Preliminary Process Flow diagram
This is anticipated process flow based on preliminary bill of material and product/Process assumptions.
1.11 Preliminary Identification of special product and Process Characteristics
This includes identification of Special or critical product and Process characteristics. Following inputs shall be taken for deriving special product and process characteristics.
- Product and Process Assumptions based on customer needs and expectations.
- Reliability Goals
- Similar part FMEA
1.12 Product Assurance Plan
The Product assurance plan translates design goals into design requirements and is based on customer needs and expectations.
It lays the framework for various activities to be conducted and defines various milestones.
1.13 Management Support
Management standard is one of the most critical prerequisites for effective implementation of any standard or program.
APQP process asks for regular management involvement through reviews at a fixed frequency. In these reviews support related to resources could be requested.
Phase 2 : Product Design and Development
This phase covers the elements of the planning process during which design features and characteristics are developed into a near-final form. The steps include prototype build to verify that the product or services meet the objective of the Voice of the customer.
At this stage of the process, a preliminary feasibility analysis will be made to assess the potential problems that could occur in mass production.
Inputs for the Phase 2
1.7 Design Goals
1.8 Reliability and Quality Goals
1.9 Preliminary Bill of Materials
1.10 Preliminary Process Flow diagram
1.11 Preliminary Identification of special product and Process Characteristics
1.12 Product Assurance Plan
1.13 Management Support
Design Outputs from the Phase 2
2.1 Design Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
DFMEA is an analytical tool to assess the probability of design failure as well as the effect of such failure.FMEA is an important input to the APQP process as it provides potential gaps and hence improvement scope in product or process at the design stage itself.
2.2 Design of Manufacturability and Assembly
Design for Manufacturability and assembly is a process designed to optimize the relationship between design function, manufacturability, and ease of assembly.
Design for manufacturability and assembly shall at minimum consider the following parameters
- Design,concept,function and sensitivity to manufacturing variation.
- Manufacturing and/or assembly process.
- Dimensional Tolerances
- Performance Requirements
- Number of Components
- Process adjustments
- Material Handling
2.3 Design Verification
Design verification verifies that the product design meets customer requirements derived from the activities described in the previous phase.
2.4 Design reviews
Design reviews are regularly scheduled CFT meetings led by the design team. Design reviews act as an important mechanism to avoid problems and misunderstandings. Also, it provides a mechanism to monitor progress, report to management, and obtain customer approval whenever required.
2.5 Prototype Build-Control Plan
The Prototype Build Control plan includes a description of the dimensional measurements, material, and functional tests that will occur during the proto build.
2.6 Engineering drawings(including Math Data)
Drawing should be reviewed to determine if there is sufficient information for the dimensional layout of the individual parts. Control or datum points shall be clearly defined to make sure those are captured in gauge and equipment design.
2.7 Engineering Specification
In this step, a detailed review and understanding of the controlling specifications are required. It helps the team identify the functional, durability, and appearance requirements of the subject component or assembly.
2.8 Material Specifications
This step involves a review of material specifications.
2.9 Drawing and Specification Changes
Wherever drawing specification changes are required, it is important that the product planning team shall properly communicate and document those changes.
APQP Outputs from the Phase 2
2.10 New Equipment,Tooling and Facilities Requirement
The DFMEA, product assurance plan, and/or design reviews may identify new equipment and facilities including meeting capacity requirements. Organization’s product quality planning Team should address these requirements by adding the items to the timing chart.
Also, these activities shall be monitored on regular basis to ensure proper and timely implementation.
2.11 Special Product and Process Characteristics
In Phase 1 product quality planning team identified preliminary special product and process characteristics. In this phase, the team should revisit them and finalize the list of product and process special characteristics.
For this Team should revisit customer-specific requirements and once the parameters are finalized they should be incorporated into the control plan
.
2.12 Gages/Testing Equipment requirements
Gauges/testing equipment requirements may also be identified at this time and the same should be added in the timing chart.
2.13 Team Feasibility Commitment and Management Support
The organization’s product quality planning team must assess the feasibility of the proposed design at this time.
Customer design ownership doesn’t mean that the supplier should not assess the design feasibility, the team must be satisfied that the proposed design can be manufactured, assembled, tested, packaged, and delivered in sufficient quantities on schedule at an acceptable cost to the customer.
Phase 3 : Process Design and Development
The objective of this phase is to ensure the comprehensive development of an effective manufacturing system.
This phase discusses the major features of developing a manufacturing system and its related control plan to achieve quality products.
Input for Phase 3
2.1 Design Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
2.2 Design of Manufacturability and Assembly
2.3 Design Verification
2.4 Design reviews
2.5 Prototype Build-Control Plan
2.6 Engineering drawings(including Math Data)
2.7 Engineering Specification
2.8 Material Specifications
2.9 Drawing and Specification Changes
2.10 New Equipment, Tooling, and Facilities Requirement
2.11 Special Product and Process Characteristics
2.12 Gages/Testing Equipment requirements
2.13 Team Feasibility Commitment and Management Support
Output From Phase 3
3.1 Packaging Standards and Specifications
At this stage customer requirements related to packaging should be incorporated into any packaging specification for the product. In all cases, the packaging design should assure that the product performance and characteristics will remain unchanged during packing transit and unpacking.
3.2 Product/Process Quality System Review
The organization’s product quality planning Team should review the manufacturing site(s) quality management system. Any additional controls and/or procedural changes required to produce the product should be updated, documented, and included in the manufacturing control plan.
3.3 Process Flow Chart
The process flow chart is a diagrammatic view of the current process; it helps visualize and focus on the complete process rather than individual steps. Process flow chart acts as input for PFMEA and control plan
3.4 Floor Plan Layout
The floor plan should be developed and reviewed to determine the acceptability of important control items such as inspection points, control chart location, the applicability of visual aids interim repair stations, and storage areas to contain non-conforming material.
All material flow should be keyed to the process flowchart and process control plan.
3.5 Characteristic Matrix
Characteristic matrix is a recommended analytical technique for displaying the relationship between process parameters and manufacturing stations.
3.6 Process Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
PFMEA is a structured analytical tool that helps identify and prioritize potential modes of failure in a manufacturing or assembly process at the system, subsystem, or component level.
PFMEA should be conducted during product quality planning and before beginning production.
To read in details about PFMEA: Click Here
3.7 Pre-Launch Control Plan
Pre-launch control plans include a description of dimensional, material, and functional controls that the process has in the pre-launch phase i.e. after prototype and before full production.
The pre-launch control plan should include additional process and product controls for validating process robustness before the mass production stage
Additional controls include but are not limited to :
- Increased frequency of inspection
- Increased in process and final checkpoints
- Statistical evaluations
- Enhanced audits
To read in detail about how to make control plan: Click Here
3.8 Process Instructions
The organization’s product quality planning team shall ensure that process instructions are documented in such a manner that it provides sufficient understanding and details of the process for all personnel who have direct responsibility for the operation of the various processes.
The following act as the input for making process instructions
- FMEAs
- Control plans
- Engineering drawings
- Process flow chart
- Floor plan layout
- Characteristics matrix
- Packaging standards and specification
- Process parameters
- Product quality planning teams expertise add knowledge of the process and product
- Handling requirement
- Skill of operators of the process
3.9 Measurement System Analysis Plan
A measurement systems analysis (MSA) is a thorough assessment of a measurement process, and typically includes a specially designed experiment that seeks to identify the components of variation in the measurement process.
The Organisation’s product quality planning Team should ensure that a plan to accomplish the required measurement system analysis is developed covering all checking AIDS.
To read further about MSA: Click Here
3.10 Preliminary Process Capability Study Plan
SPC stands for statistical process control. SPC is the use of statistical methods or SPC tools to measure, collect and analyze data to improve and control any manufacturing process or method for desired process output.
The organization’s product quality planning Team should ensure that a plan for preliminary process capability shall be developed covering all special characteristics identified in the control plan.
3.11 Management Support
The organization’s product quality team shall ensure that regular formal reviews with top management are conducted at end of each phase. It helps keep management involved and provides a platform to seek help in the resolution of any open issues.
Phase 4 : Product and Process validation
In this phase, the main objective is to validate the manufacturing process through a detailed evaluation of significant production run.
The product quality planning team shall ensure that the control plan, process flow diagram, and process instructions are followed during the significant production run. Also, they should validate whether or not the products manufactured in the significant production Run meet customer requirements.
Inputs for Phase 4
3.1 Packaging Standards and Specifications
3.2 Product/Process Quality System Review
3.3 Process Flow Chart
3.4 Floor Plan Layout
3.5 Characteristic Matrix
3.6 Process Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
3.7 Pre-Launch Control Plan
3.8 Process Instructions
3.9 Measurement System Analysis Plan
3.10 Preliminary Process Capability Study Plan
3.11 Management Support
Outputs from Phase 4
4.1 Significant Production Run
The significant production Run is the first Big Lot prepared using production tooling, production equipment, production environment, facility, production gauges, and production rate. The significant production run is the validation of the effectiveness of the manufacturing process. The minimum quantity for a significant production Run is usually set by the customer but can be exceeded by the organization’s production quality planning team.
following are the outputs expected from the significant production run
- Preliminary process capability study
- Measurement system analysis
- Peak production rate
- Production part approval
- Packaging evaluation
- First time capability
- Quality planning sign off
- Sample production parts
- Master samples
4.2 Measurement System Analysis
The data collected during a significant production Run is Used to take the decision whether or not the process is acceptable. Hence the measurement system used to collect the data must be analyzed.
Measurement system analysis is used for the same.
4.3 Preliminary Process Capability Study
The preliminary process capability study should be performed on characteristics identified in the control plan. The study provides an assessment of the readiness of the process for production.
4.4 Production Part Approval
The purpose of PPAP is to provide evidence that the supplier has completely understood customer requirements and has the potential to produce products consistently meeting these requirements at the required production rate.
4.5 Production Validation testing
Production validation testing refers to the test conducted to validate whether or not a product meets all customer-defined engineering specifications.
4.6 Packaging Evaluation
Packing evaluation is the validation conducted by the product quality planning team to make sure that there is no damage to the product while normal transportation does not have any adverse environmental factors.
4.7 Production Control Plan
The production control plan is a logical extension of the pre-launch control plan. The production control plan is used for mass production, Including all the learning since the pre-launch Phase.
4.8 Quality Planning Sign-off and management Support
Organization’s product quality planning Team should perform a review at the manufacturing location and coordinate a formal sign-off.Sign-off indicates to the management that appropriate Apqp activities have been completed. Sign-off occurs prior to the first product shipment.
Phase 5 : Feedback,Assessment and Corrective Action
Quality planning does not end with the process and product validation. It is the component manufacturing stage where output can be evaluated when common and special causes of variation are present in the process.
The objective of this phase is to take feedback from the manufacturing stage and improve the current process.
Inputs for Phase-5
4.1 Significant Production Run
4.2 Measurement System Analysis
4.3 Preliminary Process Capability Study
4.4 Production Part Approval
4.5 Production Validation testing
4.6 Packaging Evaluation
4.7 Production Control Plan
4.8 Quality Planning Sign-off and management Support
Outputs from Phase-5
5.1 Reduced Variation
Control charts and other tools shall be used to monitor the process for variation. Actions should be taken to reduce these variations. The focus should not only be to reduce special causes of variation but the focus should also be to reduce the common causes of variation.
The elimination or reduction of a common cause may provide additional benefits of lower costs.
5.2 Improved Customer Satisfaction
5.3 Improved Delivery and Service
5.4 Effective Use of Lessons learned/Best Practices
During product quality planning there are many learnings that need to be captured. They can be captured in the following forms
- Review of things gone right/ things gone wrong.
- Data from warranty and other performance metrics
- Corrective action plans
- DFMEA and PFMEA studies
When to perform APQP?
It is recommended to perform APQP in the following two cases. In the below-mentioned cases, the only difference is that different APQP events are applicable for each of them.
New Product Development
It is used for planning product quality for completely new parts. New part in the sense that its development has to be done from scratch and that it’s not a modification in an already existing part.
Changes in Product or Process Post SOP(Start of Production)
If there are changes in product or process post SOP, it is recommended to follow APQP guidelines. But the number of APQP events applicable may vary from the case of new Product Development.
Changes could be one of the followings
- Changes in drawing.
- Process Parameter Change
- Process Sequence Change
- Plant Location Change
- Supplier Change
This list is only indicative and not exclusive.
What are the benefits of APQP?
APQP is a planning and communication tool, helping OEM’s communicate their requirements in a structured and clear manner.
APQP is beneficial both for the Customer and the Supplier. It brings clarity in the sense of what needs to be done, and what should not be done.
APQP allows the team to take action on the risk instead of having to wait for defects to occur in trials or worse, in the hands of the customer.
Benefits for (OEM) or Customer are as follows
- Provides a framework for communicating all its requirements to the Supplier.
- Reduces the product development time.
- Helps achieve the goal of First time right.
- Reduces risk of warranty claims.
- Since APQP is a standardized process,it reduces the effort required by OEMs to manage multiple suppliers.
- Helps OEMs work with Suppliers across the globe.Standardized framework supports working with multilingual suppliers.
- Helps increase supplier accountability.
Benefits for Suppliers are as follows
- Clear Understanding of Customer Requirement related to Product and Process.
- Avoids repetition of defects,hence costs less.
- Since APQP promotes the concept of continual improvement,hence it pushes Suppliers to become a better version of themselves every time.
- Better Quality,in less time and less cost results in a happy and satisfied Customer.
FAQ
What is the full form of AIAG?
AIAG stands for Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG). It is a not-for-profit association founded in 1982 and is based in Southfield, Michigan.
What are the 5 core tools?
The five core tools are as follows:
- Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA)
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Product Part Approval Process (PPAP)
These tools are recommended to be used in the same sequence they are mentioned in.
What is the latest version of APQP in Supply?
The second version or edition of the APQP manual is in supply currently i.e. APQP-2 – (2008).
What’s the Difference Between APQP and PPAP?
PPAP is a part of the APQP process.APQP includes planning, designing, validation, and Feedback, whereas PPAP is more about the validation part of APQP.
What industries use APQP?
APQP was developed by AIAG for the Automotive sector, but now it is used by various manufacturing industries such as Healthcare, Agri-Machinery, etc.
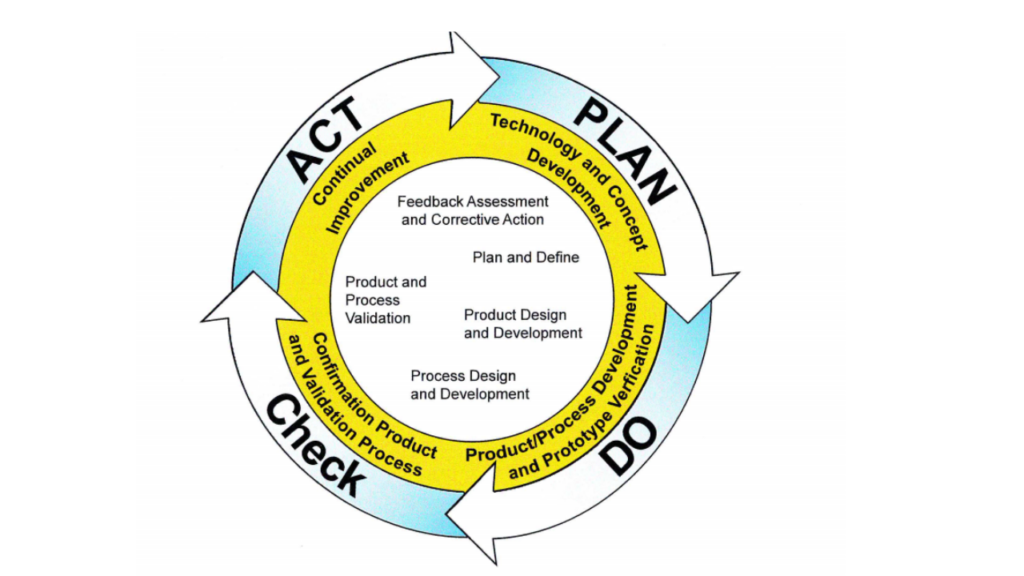
Is APQP a PDCA cycle?
Yes, APQP can be described as a PDCA Cycle. Since it is a practical application of PDCA to the project management process.
Phase 1 : Plan
Phase 2, Phase 3: Do
Phase 4: Check
Phase 5: Act